Scaly Dermatoses
Overview
Seborrheic dermatitis
What is seborrheic dermatitis? — Seborrheic dermatitis is a skin condition that causes redness, scaly or flaky patches, and sometimes itching. It usually affects areas with many oil glands. These include the scalp, face, upper chest, and back. Dandruff is a mild type of seborrheic dermatitis.
Seborrheic dermatitis is common in babies. It is called “cradle cap”. Cradle cap can cause redness and greasy yellow scales on the head. It can also cause red patches and greasy scales on the face, diaper area, or other areas.
What are the symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis? — In adults, common symptoms include:
●Redness
●Scaly patches on the skin that can look oily or greasy
●White scales or flakes on the head or hair – This is the most common symptom of dandruff.
●Mild itching
●Crusty, yellow material on the eyelashes and eyelid redness
Stress can make seborrheic dermatitis worse. It often gets worse in winter, when the weather is cold and dry. It can get better in summer.
Is there a test for seborrheic dermatitis? — No. There is no one test for seborrheic dermatitis. A doctor or nurse can usually tell if someone has it by doing an exam and asking questions.
If your doctor is not sure you have seborrheic dermatitis, he or she might do a skin biopsy. In this test, the doctor takes a small sample of skin from an affected area. Another doctor looks at the sample under a microscope to see if it is seborrheic dermatitis.
How is seborrheic dermatitis treated? — Treatments include:
●Skin creams and ointments – These can help stop itching and redness. They might contain medicines that kill fungus (called “antifungal medicines”), steroid medicine, or other medicines. These are not the same as the steroids some athletes take illegally.
●Shampoos with antifungal or steroid medicine
Cradle cap usually goes away on its own. This can take a few weeks or months. If you have questions, ask your baby’s doctor or nurse.
Is there anything I can do on my own to feel better? — Yes. Depending on the type of seborrheic dermatitis, there are different treatments you can try. They include:
●Using an over-the-counter anti-dandruff shampoo (sample brand names: Selsun, Head and Shoulders). Use it every day until you see less dandruff. After that, use it every other day or twice a week. Leave it on your hair for 5 or 10 minutes. Then rinse your hair, making sure you get all the shampoo out. If your dandruff does not get better after 4 to 6 weeks, try a different anti-dandruff shampoo. If your symptoms get worse, see your doctor or nurse.
●Using an over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream (sample brand names: Ala-Cort, Cortaid) to help stop redness and itching on the face or body. Use it 1 or 2 times a day until the symptoms get better. If they do not get better after 2 weeks, see a doctor or nurse.
If your baby has cradle cap, you can try:
●Washing the area with baby shampoo and using a soft toothbrush or fine-tooth comb to remove scaly skin.
●Putting a small amount of oil (such as petroleum jelly, vegetable oil, mineral oil, or baby oil) on your baby’s head to loosen scaly skin. You can leave this on overnight, if needed. Next, brush the baby’s scalp gently with a soft brush to remove scales. Then wash the area with regular baby shampoo (not baby shampoo with medicine in it).
If your baby still has cradle cap after you try these things, talk to your baby’s doctor or nurse.
picture 3: Seborrheic dermatitis
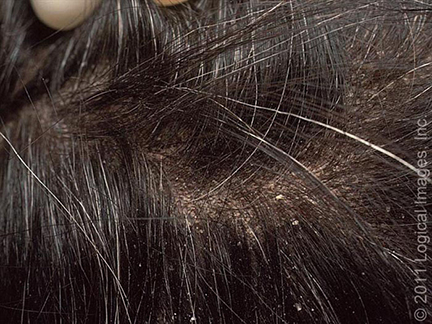
Dandruff is a mild form of seborrheic dermatitis. It causes white scales or flakes on the head or hair.
Psoriasis
What is psoriasis? — Psoriasis is a skin condition that can make parts or all of your skin red, thick, and flaky. In people with dark skin tones, the psoriasis spots might look purple, dark brown, or dark gray. The flakes on top of psoriasis are usually silver or white and thick.
Doctors do not know exactly what causes psoriasis to suddenly appear. Certain things might make some people more likely to get psoriasis, like having family members with the condition.
What are the symptoms of psoriasis? — The symptoms of psoriasis can include:
●Areas of skin that are dry, red, or dark, and that are usually covered with silvery or white flakes
●Rashes on the scalp, genitals, or in skin folds (like in the armpit, groin, or under the breasts)
●Itching
●Nail changes that make the fingernails or toenails look pitted, crumbly, or different in color
Psoriasis has an emotional effect, too. People with the condition often feel embarrassed by their skin, and some get depressed or anxious. If you have these problems, mention them to your doctor or nurse. You might feel better with counseling or another type of mental health treatment.
Is there a test for psoriasis? — Your doctor or nurse should be able to tell if you have psoriasis by looking at your skin and by asking you questions. In rare cases, doctors take a small sample of skin to check if psoriasis is the problem.
What can I do to reduce my symptoms? — Use unscented thick moisturizing creams and ointments to keep the skin from getting too dry.
How is psoriasis treated? — There are treatments that can relieve the symptoms of psoriasis. But the condition cannot be cured.
Treatments for psoriasis come in creams and ointments, pills, or shots. There is also a form of light therapy called “phototherapy” that can help with psoriasis. Treatments for psoriasis work by slowing the growth of skin, controlling the immune response that causes psoriasis, or both. Most people need to try different treatments or combinations of treatments before they figure out what works best. The medicines that are used most often are called steroids. These medicines are applied to the skin.
What is psoriatic arthritis? — Psoriatic arthritis is a form of arthritis that can affect some people with psoriasis. It causes pain and swelling in the joints. It is important to tell your doctor or nurse if you have psoriasis and notice pain in your joints.
People with psoriatic arthritis can take medicines to reduce pain and swelling. Exercise and physical therapy can also help. Plus, some of the same medicines that help with the skin problems caused by psoriasis also help with psoriatic arthritis.
picture 1: Plaque psoriasis
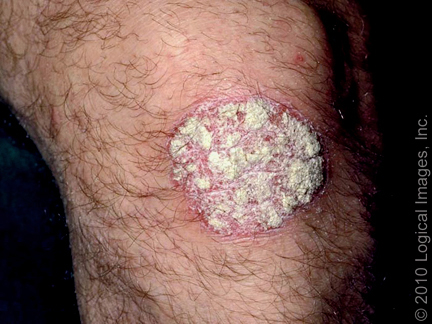
Plaque-type psoriasis causes the skin to form red, raised, scaly areas.
picture 2A: Nail psoriasis
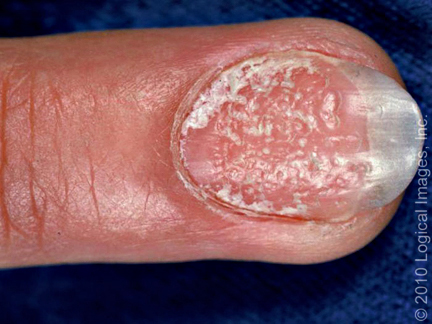
People with psoriasis sometimes develop pits on their nails, like the ones shown here.
picture 2B: Nail psoriasis
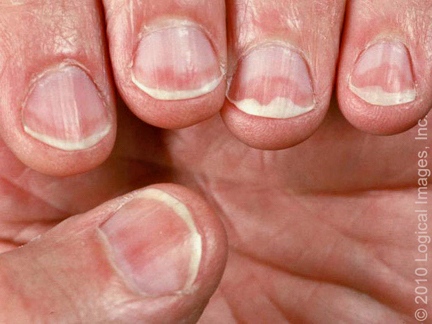
The nails of people with psoriasis sometimes develop tan-brown color changes, like those shown here.
Selenium Sulfide
What is selenium sulfide topical?
Selenium sulfide is an antifungal medication. It prevents fungus from growing on your skin.
Selenium sulfide topical (for the skin) is used to treat dandruff, seborrhea, and tinea versicolor (a fungus that discolors the skin).
Shampoo (OTC 1%): Massage shampoo into wet scalp then rinse thoroughly. Use at least twice weekly for best results.
How should I use selenium sulfide topical?
Use this medicine exactly as directed on the label, or as prescribed by your doctor. Do not use it in larger amounts or for longer than recommended.
Shake the selenium sulfide foam, lotion, or shampoo well just before each use.
Wash your hands after applying the foam or lotion.
Rinse the shampoo thoroughly. Do not leave it in your hair for an extended period of time. Selenium sulfide topical shampoo is generally not for daily use. Follow the directions on the label, or your doctor’s instructions.


